- Início
- "
- veterinário Clínico
- "
- Cirurgia
- "
- Derrame uterino em ouriço - exame clínico de ultrassom
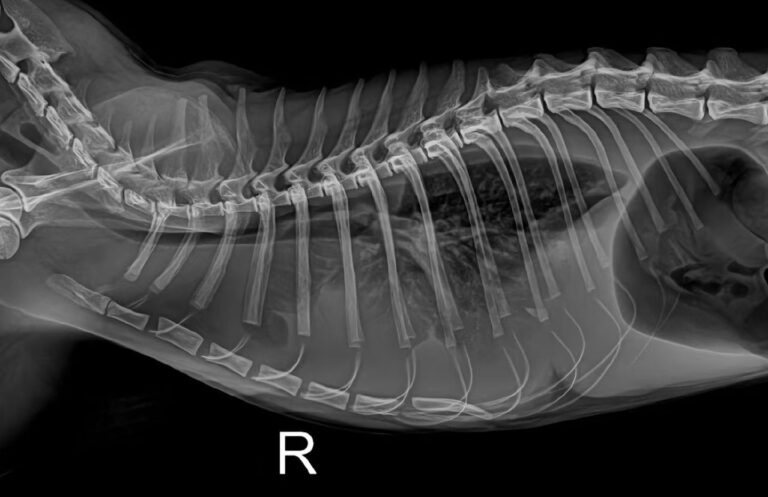
Derrame uterino em ouriço - exame clínico de ultrassom
Patient: Hedgehog 4 years old, weight 400g, unneutered female.
Ultrasonography: probed with the microconvex probe L13-3NS of the Mindray Animal Medical Vetus E7: the fluid-filled uterus was clearly demonstrated.
Analysis:
1. Common uterine diseases in hedgehogs: uterine pus accumulation, blood accumulation
2. Uterine pus accumulation in hedgehogs may be accompanied by other symptoms such as loss of appetite, abdominal distension, and discharge. Uterine pus accumulation is an emergency in unspayed females and requires immediate treatment, which usually includes surgical removal of the uterus and ovaries.

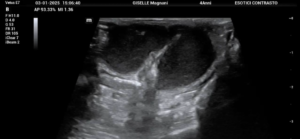
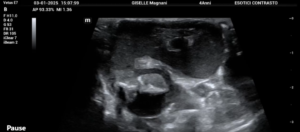
I. Ultrasonographic features and pathological inferences
| Indicators | Ultrasound performance | Suggestive Pathology |
| Uterine morphology | Significant dilatation (normal hedgehog uterus <3mm in diameter) | Effusion dilatation (abnormal volume) |
| Intracavitary echo | homogeneous hypoechoic (no separation or sediment) | Accumulation of blood (hemometra) is more likely |
| or mixed echoes (purulent debris/gas) | Pus accumulation in the uterus (pyometra) possible | |
| Uterine wall structure | Thickness >2mm (normal S1mm) | Inflammatory or proliferative lesions (e.g. cystic endometrial hyperplasia) |
Key differential points:
Pyometra: often associated with fever, purulent vaginal discharge, and ultrasound visualisation of intracavitary hyperechoic granules (pus);
Hemometra: mostly due to bleeding from the reproductive tract (e.g. hormonal disorders, trauma), more homogeneous fluid, no signs of infection.
II. Special considerations for hedgehog uterine disease
High prevalence factors:
Risk of uterine disease in unspayed female hedgehogs >60% (especially in individuals >2 years old);
Hedgehogs have irregular ovarian cycles and are susceptible to hormone-dependent lesions.
Secondary risks:
Uterine rupture (high fluid pressure);
Septicaemia (if infectious pyometra).
III. Emergency treatment
Steps to confirm the diagnosis:
Fine needle aspiration (FNA): aseptic collection of uterine fluid for cytology (pus cells/red blood cells) and bacterial culture;
Routine blood count: white blood cell count >20×10⁹/L suggests infection (supports pyometra).
Surgical treatment:
Ovariohysterectomy (OVH):
Leia os principais artigos
Derrame uterino em ouriço - exame clínico de ultrassom
O acúmulo de pus uterino em ouriços pode ser acompanhado de outros sintomas, como perda de...
Leia maisHemoplasmose felina sem protocolos de análise bioquímica
O micoplasma destrói as membranas dos eritrócitos → hemólise intra e extravascular → hemólise imunomediada secundária (IMHA) →...
Leia maisCaso de efusão pleural em um gato: processo do programa de diagnóstico de emergência
As causas comuns de efusão pleural em gatos são doenças cardíacas (por exemplo, cardiomiopatia hipertrófica), tumores (por exemplo, ....
Leia maisPor que esterilizar gatos? Momento ideal e cuidados pós-operatórios
A esterilização é uma responsabilidade fundamental para os donos de animais de estimação, melhorando a saúde dos felinos e reduzindo o número de animais de rua...
Leia maisEquipamento de geração de imagens em destaque
Com foco em equipamentos de imagem veterinária de alta qualidade, integrando tecnologia inovadora, diagnóstico preciso, desempenho e custo-benefício