- Home
- »
- innovative tech
- »
- DeepSeek AI Assists in Parkinson’s DBS Surgery
DeepSeek AI Assists in Parkinson’s DBS Surgery
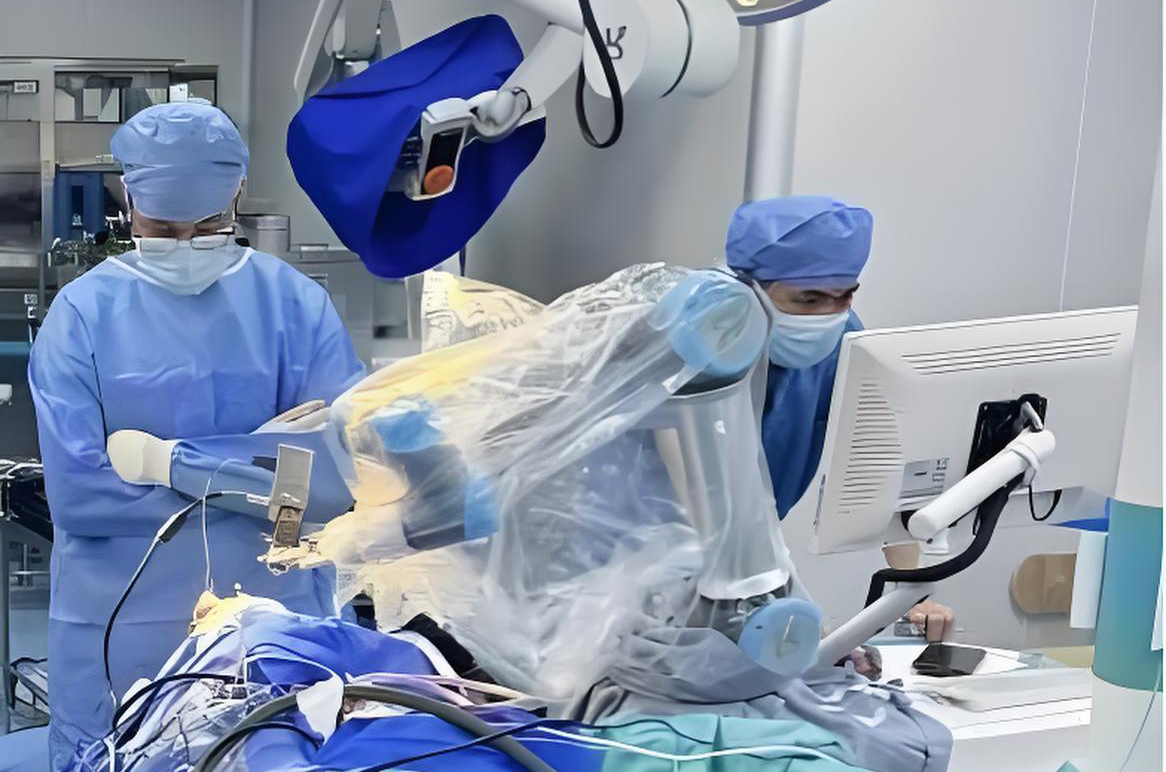
The Neurosurgery team at the First Affiliated Hospital of Guangdong Pharmaceutical University has successfully performed a DeepSeek-assisted robotic-guided bilateral deep brain stimulation (DBS) implantation surgery for a Parkinson’s disease (PD) patient from Hong Kong. This marks the hospital’s first high-complexity neurosurgical procedure utilizing AI-powered medical intelligence since deploying the DeepSeek-R1 AI healthcare model.
The 65-year-old patient from Hong Kong has been battling Parkinson’s disease for 23 years. Initially presenting with mild tremors in the right hand, her symptoms progressively worsened to uncontrolled bilateral tremors, followed by generalized rigidity and loss of ambulation. She had been wheelchair-bound for three years before seeking neurosurgical consultation at the hospital.
Under the leadership of Associate Chief Neurosurgeon Dr. Zhou Hui, a multidisciplinary team—including specialists from neurology, radiology, and anesthesiology—conducted a comprehensive evaluation of the patient’s condition. Utilizing the newly implemented DeepSeek AI-driven diagnostic system, the team integrated the patient’s medical history, neuroimaging data, and pharmacological responses to determine the optimal surgical approach and predict postoperative DBS outcomes. Ultimately, the team elected to proceed with bilateral DBS implantation using robotic-guided stereotactic precision targeting.
During the procedure, the neurosurgical team employed a robotic navigation system to fuse MRI and CT imaging, meticulously mapping a trajectory to the bilateral subthalamic nuclei (STN) while avoiding critical vasculature and functional brain regions. With an accuracy margin of 0.15 mm, the electrodes were precisely implanted into the target regions, and the surgery was successfully completed.
By the third postoperative day, the patient exhibited a marked reduction in involuntary tremor amplitude and frequency. Additionally, the duration of symptom relief provided by pharmacological treatment extended from 3.5 hours preoperatively to over 6 hours. Overwhelmed with emotion, the patient expressed, “I feel like I have regained control over my body!”
The Role of AI in Modern Neurosurgery: What Can AI Achieve?
Dr. Zhou Hui explained that Parkinson’s disease is a common neurodegenerative disorder characterized by bradykinesia, tremors, and rigidity, often accompanied by cognitive impairment, sleep disturbances, and other complications that severely impact patients’ quality of life. While there is currently no cure for Parkinson’s, pharmacologic therapy remains the primary treatment. However, as the disease progresses, medication efficacy diminishes, making deep brain stimulation (DBS) an essential intervention for patients in the advanced stages.
DBS involves implanting electrodes in specific brain regions to deliver electrical impulses that modulate aberrant neural activity, thereby alleviating motor symptoms and improving overall function. The success of DBS, however, hinges on accurate preoperative evaluation and precise intraoperative targeting. Conventional stereotactic methods rely heavily on the surgeon’s expertise and manual adjustments, introducing a margin of error.
In this case, the DeepSeek AI healthcare model played a pivotal role in optimizing surgical planning. By integrating multimodal data—including medical history, neuroimaging, and pharmacodynamic response—DeepSeek facilitated the development of a personalized perioperative management strategy and outcome prediction model. Additionally, the surgical team replaced traditional stereotactic techniques with high-precision robotic navigation. AI algorithms enabled seamless fusion of MRI and CT scans, allowing the construction of a highly accurate “deep brain electrode implantation target map.” This comprehensive AI-assisted approach not only optimized surgical steps and predefined the most precise trajectory—maintaining an error margin within 0.2 mm—but also provided contingency strategies for potential intraoperative challenges, ensuring meticulous planning and execution at every stage of the procedure.
Dr. Zhou emphasized that the synergy between DeepSeek’s AI-driven preoperative analysis and robotic-assisted precision targeting provided a “dual safeguard” for the surgical outcome. This successful case signifies a major advancement in the hospital’s capabilities in DBS therapy for Parkinson’s disease, setting new benchmarks in both efficiency and precision. Moving forward, the neurosurgery team aims to expand DeepSeek’s applications to a broader spectrum of neurological disorders, driving the evolution of neurosurgical interventions toward greater accuracy, safety, and efficacy—ultimately enhancing patient care.
Source: Yangchengpai/mtech