- Accueil
- "
- vet Clinical
- "
- Médecine interne
- "
- Hémoplasmose féline sans protocole d'analyse biochimique
Hémoplasmose féline sans protocole d'analyse biochimique
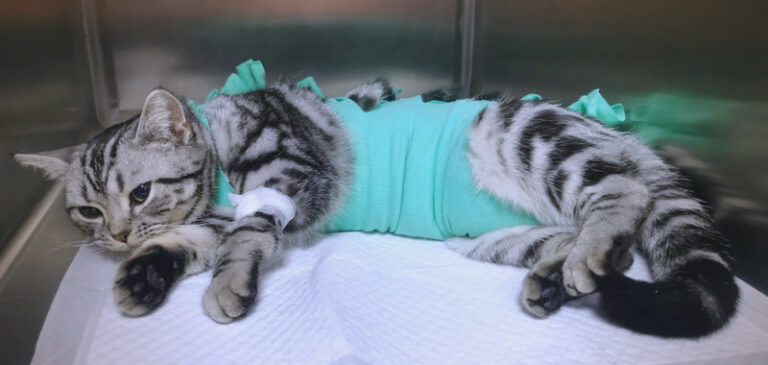
Case: A cat named mike was diagnosed with Feline Hemoplasmosis.
Vital Signs Presentation:
Severe dehydration, severely pale mucous membranes, depression, hypothermia, tachycardia, tachypnea, severe runny nose, blepharospasm (spasms of the eyelids), conjunctival oedema (swelling of the conjunctiva), severe perforated corneal ulcers
Clinical Diagnosis:
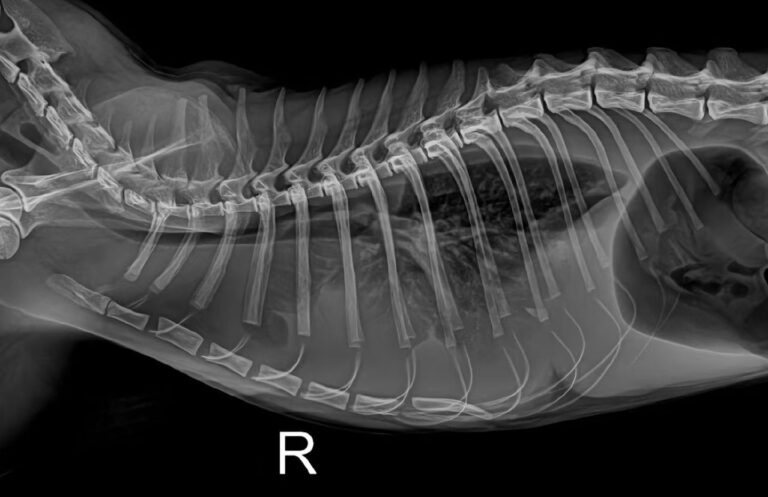
Ultrasound: rapid detection of splenomegaly and mild hepatic steatosis.
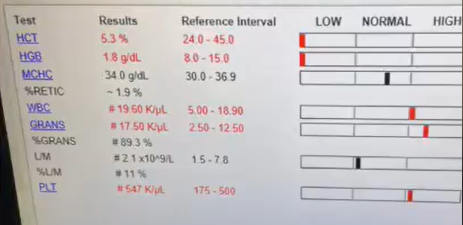
CBC findings:
Haemoglobin (HB): 1.8 g/dL
Haematocrit (HCT): 5.3%
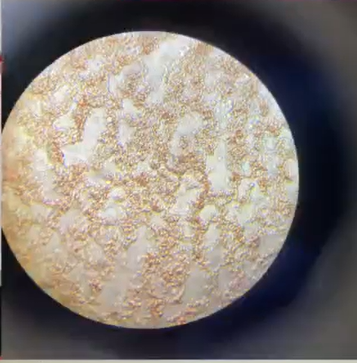
Blood smear: positive for mycoplasma.
Slide agglutination test: positive, indicating secondary immune-mediated haemolytic anaemia (IMHA).
I. Definition of the disease and types of pathogens
Pathogen:
Main types:
Mycoplasma haemofelis (strongly pathogenic, parasitises the surface of erythrocytes and causes severe haemolysis);
Candidatus Mycoplasma haemominutum (weakly pathogenic, often latent infection);
Candidatus Mycoplasma turicensis (intermediate pathogenicity).
Routes of transmission: flea bites (primary), bites, blood transfusions, vertical transmission.
Pathogenesis:
Mycoplasma destroys erythrocyte membranes → intra- and extravascular haemolysis → secondary immune-mediated haemolysis (IMHA) → anaemia, tissue hypoxia.
| II. Typical clinical manifestations | ||
| Systems | Symptoms. | Corresponding presentation of Mike’s case |
| Circulatory System | Tachycardia (>220bpm), pale mucous membranes | Tachycardia, mucosal pallor (HCT 5.3%) |
| Respiratory System | Shortness of breath (compensating for hypoxia) | Shortness of breath |
| Eye | Conjunctival oedema, blepharospasm (hypoxic neurological reflex) | Conjunctival swelling, blepharospasm. |
| Systemic | Depression, hypothermia (<37°C, metabolic failure) | Hypothermia, severe dehydration. |
Emergency treatment protocol in the absence of blood chemistry analysis
1. Core treatment goals:
Correction of anaemia: enhance oxygen-carrying capacity;
Clear pathogens: control mycoplasma proliferation;
Suppressing immune destruction: blocking the IMHA vicious cycle.
Emergency treatment protocol in the absence of blood chemistry analysis
1. Core treatment goals:
Correction of anaemia: enhance oxygen-carrying capacity;
Clear pathogens: control mycoplasma proliferation;
Suppression of immune destruction: blocking the IMHA vicious cycle.
2. Treatment protocol:
Whole blood transfusion (after crossmatching), target HCT ≥ 15%
Antibiotics to control pathogen proliferation
Management of complications such as corneal ulcers routine treatment
After 10 days of treatment, Mike’s body is stable, showing vigour and in good condition, with all indicators up to standard
Lire les articles du haut de la page
Hedgehog uterine effusion – ultrasound clinical examination
Uterine pus accumulation in hedgehogs may be accompanied by other symptoms such as loss of...
En savoir plusHémoplasmose féline sans protocole d'analyse biochimique
Les mycoplasmes détruisent les membranes des érythrocytes → hémolyse intra- et extravasculaire → hémolyse secondaire à médiation immunitaire (HMI) →...
En savoir plusCas d'épanchement pleural chez un chat : processus du programme de diagnostic d'urgence
Les causes courantes d'épanchement pleural chez les chats sont les maladies cardiaques (par exemple, la cardiomyopathie hypertrophique), les tumeurs (par exemple, ....) et les maladies infectieuses.
En savoir plusPourquoi stériliser les chats ? Moment optimal et soins postopératoires
La stérilisation est une responsabilité essentielle pour les propriétaires d'animaux de compagnie, car elle améliore la santé des félins et réduit le nombre d'animaux errants...
En savoir plusÉquipement d'imagerie en vedette
Se concentrer sur des équipements d'imagerie vétérinaire de haute qualité, intégrant une technologie innovante, un diagnostic précis, des performances et un bon rapport coût-efficacité.